Stainless Insights in China from February 24th to February 28th.
WEEKLY AVERAGE PRICES
| Grade | Origin | Market | Average Price (US$/MT) | Price Difference (US$/MT) | Percentage (%) |
| 304/2B | ZPSS | Wuxi | 2,030 | 0 | 0.00% |
| Foshan | 2,070 | 0 | 0.00% | ||
| Hongwang | Wuxi | 1,925 | 4 | 0.23% | |
| Foshan | 1,950 | 8 | 0.46% | ||
| 304/NO.1 | ESS | Wuxi | 1,855 | 3 | 0.16% |
| Foshan | 1,875 | 4 | 0.24% | ||
| 316L/2B | TISCO | Wuxi | 3,450 | -14 | -0.42% |
| Foshan | 3,535 | 11 | 0.33% | ||
| 316L/NO.1 | ESS | Wuxi | 3,325 | -11 | -0.35% |
| Foshan | 3,325 | 0 | 0.00% | ||
| 201J1/2B | Hongwang | Wuxi | 1,225 | 1 | 0.12% |
| Foshan | 1,225 | 11 | 1.01% | ||
| J5/2B | Hongwang | Wuxi | 1,125 | 3 | 0.28% |
| Foshan | 1,125 | 10 | 0.97% | ||
| 430/2B | TISCO | Wuxi | 1,145 | 1 | 0.13% |
| Foshan | 1,135 | 0 | 0.00% |
TREND || Stainless Steel Prices Slightly Increased, Mills Still Operating at a Loss.
Last week, stainless steel spot prices in the Wuxi market fluctuated slightly following market trends. Costs rose due to increasing raw material prices, while market arrivals remained steady. End-user demand was primarily driven by rigid demand, and inventory accumulation limited price rebounds. As of Friday, the main stainless steel futures contract price increased by US$9.7/MT from the pre-holiday level to US$1980/MT.
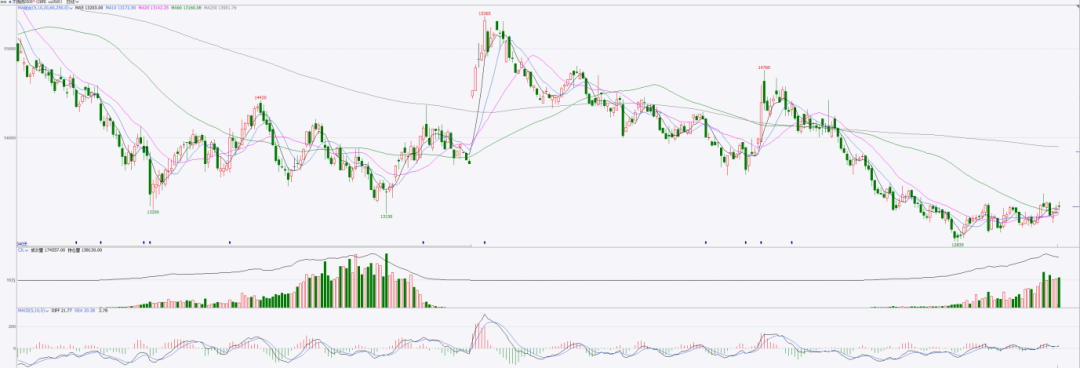
300 Series: Strengthened Expectations, Futures Prices Fluctuated Upward.
The 304 spot market remained stable last week. As of Friday, the mainstream base price for privately-owned cold-rolled 304 four-foot sheets in Wuxi was US$1890/MT, while privately-owned hot-rolled prices were US$1860/MT, both unchanged from last Friday. At the beginning of the week, futures retreated, causing lower acceptance of high-priced resources and leading to moderate market transactions. Later in the week, rising ferronickel prices and rumors of steel production control measures supported futures price recovery. However, due to high inventory pressure, merchants adjusted prices downward to stimulate sales, and lower-priced resources saw decent turnover.
200 Series: Spot Prices Followed Market Fluctuations.
The 201 series experienced mixed price movements last week. The 201J2 cold-rolled base price was US$1100/MT, while 201J1 cold-rolled and hot-rolled prices stood at US$1205/MT and US$1175/MT, respectively.
Affected by weak futures, the 201J2 cold-rolled price dropped by US$7/MT on Wednesday. As futures rebounded, market confidence improved, and by Friday, 201J1 and 201J2 cold-rolled prices both increased by US$7/MT.
400 Series: Stable Raw Material Prices, Slightly Higher Finished Product Prices.
In late February 2025, Wuxi's 430 cold-rolled prices remained stable, with mainstream spot prices fluctuating around US$1145/MT-US$1155/MT. High-chrome prices in the raw material sector remained firm, exceeding market expectations, providing stable cost support for the 400 series stainless steel.
INVENTORY || Supply Accumulation Increases Inventory Pressure.
As of February 27th, total inventory in Wuxi sample warehouses increased by 22,145 tons to 703,243 tons. Breakdown:
200 Series: 2,063 tons down to 57,932 tons.
300 Series: 19,357 tons up to 4495,740 tons.
400 Series: 4,851 tons up to 149,571 tons.
| Inventory in Wuxi sample warehouse (Unit: tons) | 200 series | 300 series | 400 series | Total |
| Feb 20th | 59,995 | 476,383 | 144,720 | 681,098 |
| Feb 27th | 57,932 | 495,740 | 149,571 | 703,243 |
| Difference | -2,063 | 19,357 | 4,851 | 22,145 |
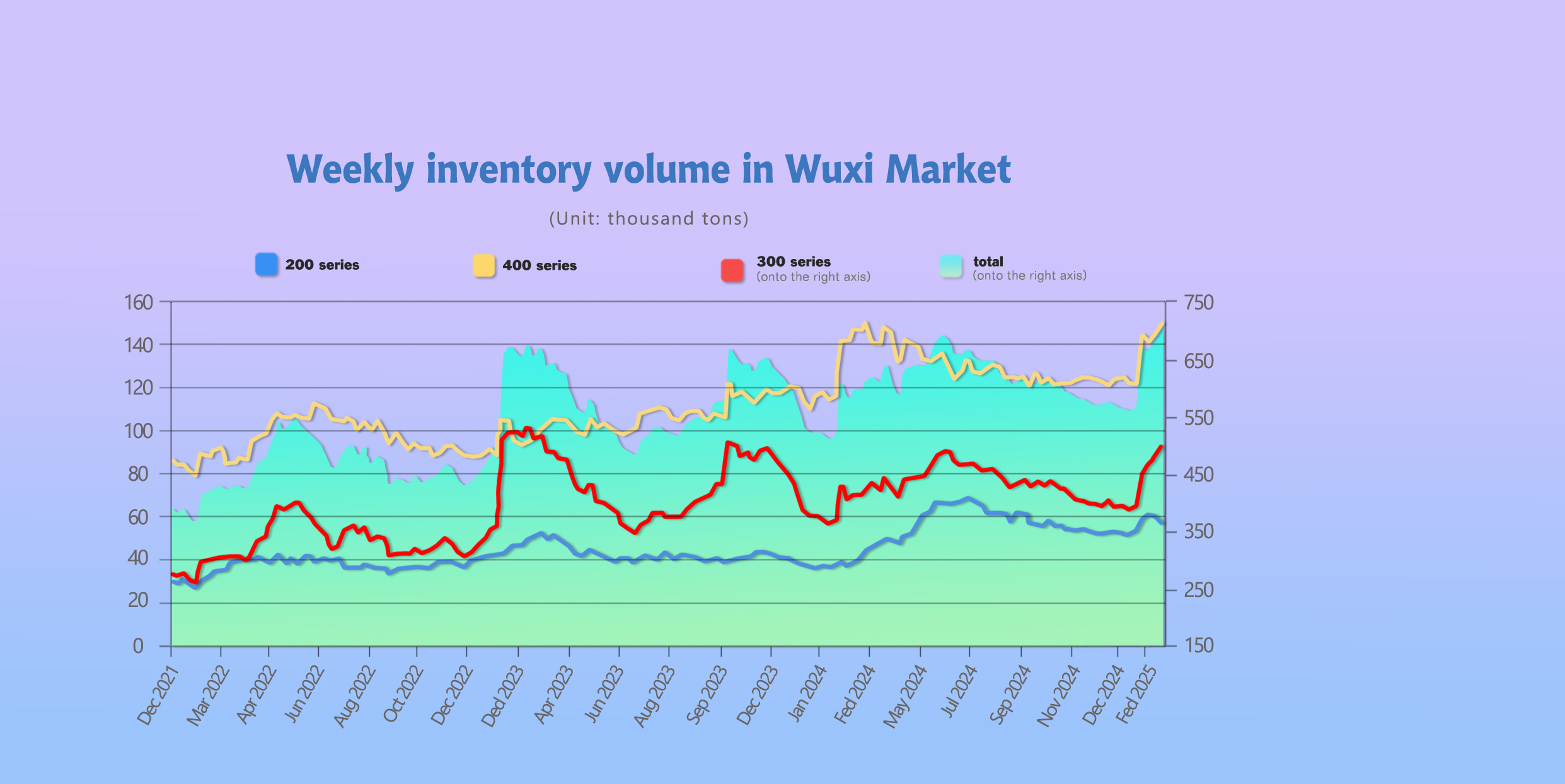
200 Series: Increased Low-Price Purchases, Slight Inventory Reduction.
This period, 200-series inventory decreased by 0.21 million tons to 5.79 million tons (cold-rolled inventory declined by 0.21 million tons, while hot-rolled inventory slightly increased). In the short term, 201J2 prices are expected to remain stable. Next week, inventory may continue to decline, with key focus on steel mill production trends and market transactions.
300 Series: Increased Warehouse Receipts, Significant Cold-Rolled Inventory Growth.
Last week, Wuxi's 300-series inventory increased by 1.94 million tons (1.13 million tons of cold-rolled and 0.81 million tons of hot-rolled) to 49.57 million tons. In terms of spot inventory structure, more Delong cold-rolled resources arrived, increasing market liquidity and maintaining the inventory growth trend. The fundamental outlook remains weak, with ongoing supply pressure and slow demand recovery. Both supply and demand are currently weak, leading to continuous inventory accumulation and limiting price rebounds. Next week, inventory is expected to grow slightly, with ongoing attention on future steel mill production and market transactions.
400 Series: Weak Supply and Demand Persist, Inventory Continues to Grow.
Last week, Wuxi's 400-series inventory increased by 0.49 million tons (0.40 million tons cold-rolled, 0.09 million tons hot-rolled) to 14.96 million tons. Continuous arrivals of JISCO cold-rolled resources and deliveries from TISCO for both cold and hot-rolled products kept supply pressure high, leading to evident inventory accumulation. Recently, 430 prices have remained stable. As demand gradually recovers, downstream purchasing activity is expected to increase, accelerating spot inventory consumption. Focus remains on March high-chrome steel bidding prices and their impact on the stainless steel market.
RAW MATERIAL || Continuous Positive Factors in February, Rising Ferronickel Prices.
In January, domestic high-nickel iron prices continued to rise. The mainstream ex-factory price was reported at US$136.8/nickel point, up US$5.5/nickel point from the previous month, a 4.28% increase. The average ex-factory price in major production areas was US$133.6/nickel point, up US$3.05/nickel point from the previous month's average of US$130.5/nickel point, a 2.34% increase.
China's high-nickel iron production remained low, while the Philippines entered the rainy season, keeping nickel ore prices firm. Domestic nickel iron factories continued to operate at a loss, reducing production motivation. Environmental inspections in northern China further reduced production. In March, high-nickel iron production is expected to rise slightly to around 210,000 tons.
In Indonesia, a local ferronickel plant's third phase shut down due to management changes and insufficient nickel ore reserves in Q1. Although the plant had some reserves in January, production was already reduced. By February, utilization had dropped to only 20-30%, potentially affecting ferronickel output by about 10,000 tons, thereby impacting China’s nickel iron imports. The mainstream ex-factory price of Indonesian ferronickel stood at US$137.5/nickel point, mainly purchased by traders.
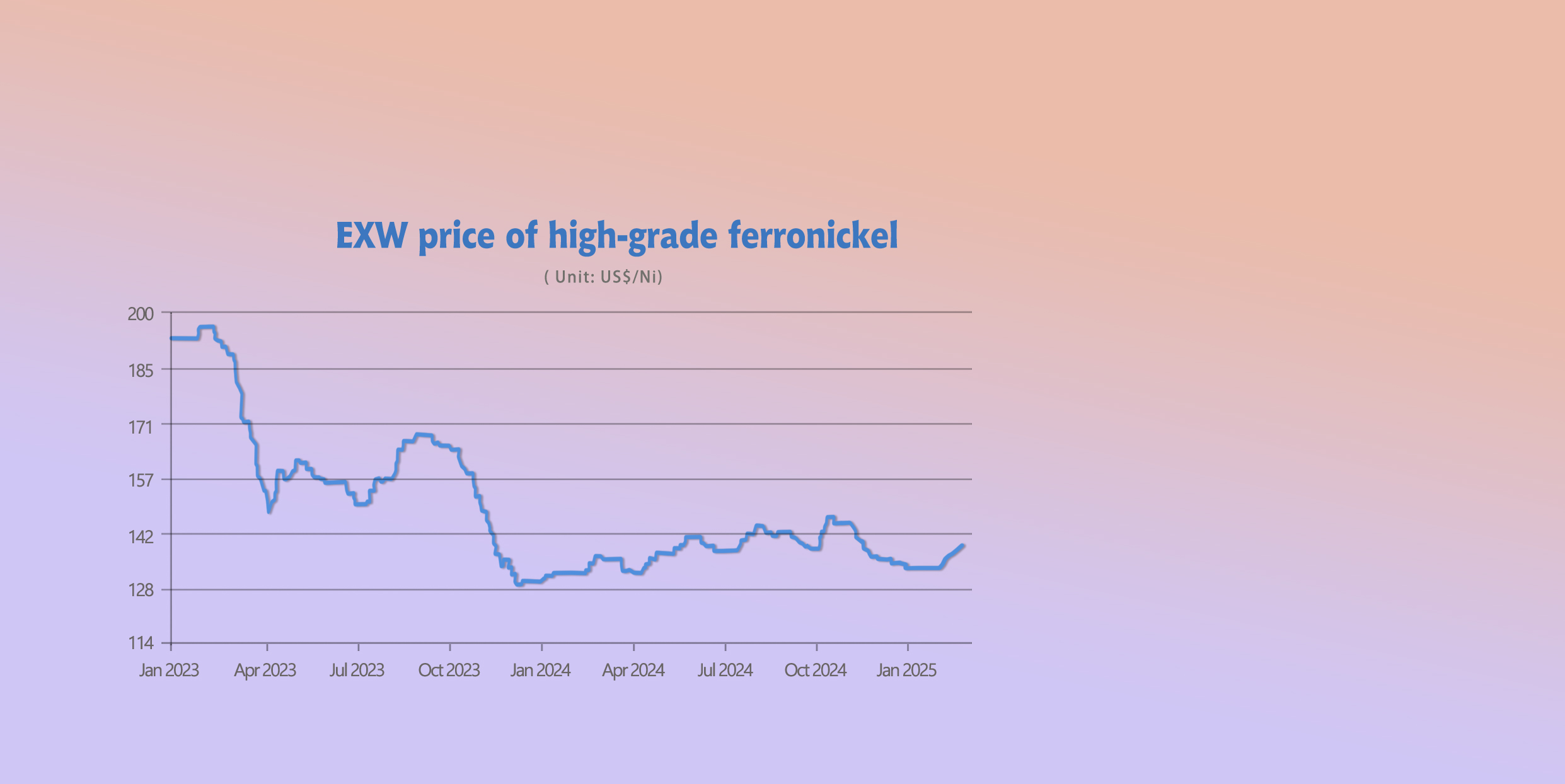
March Market Outlook.
Indonesian ferronickel production constraints will impact domestic supply, while local nickel ore premiums continue rising, supporting ferronickel prices. In February, Chinese steel mills had sufficient raw material inventories and refrained from large-scale purchases despite rising ferronickel prices. In March, mills may enter the market for restocking, leading to steady or strong ferronickel prices.
SUMMARY || Cost Support Underpins Stainless Prices.
Stainless steel spot prices fluctuated strongly last week. Stable raw material costs and thinning mill margins coincided with rising inventories and reduced warehouse receipts. Market focus remains on inventory trends, mill production adjustments, and raw material prices.
300 Series: Low mill output eases supply pressure, but weak demand sustains inventory challenges. Rising costs may curb future production. Prices expected to follow futures with mild strength.
200 Series: Beigang’s maintenance plan and firm copper/manganese costs bolster sentiment. Gradual demand recovery supports stable 201J2 prices.
400 Series: Stable production costs and moderate demand keep 430 prices steady. Inventory drawdowns remain slow.
MACRO || Global Crude Steel Output Drops 4.4% YoY in January.
Global inflation will keep extending under intertwined issues currently, such as the US's taxes which stir the global market. In China, the Two Sessions which decide the year's economic goals and policies are ongoing. Generally, Beijing will continue active fiscal policy and loose monetary policy.
On February 25, the World Steel Association reported that the crude steel production of 69 countries/regions included in its statistics reached 151.4 million tons in January 2025, marking a year-on-year decrease of 4.4%.
| Top 10 Crude Steel Producing Countries | ||
| Countries | Volume(Million Tons) | YoYΔ |
| China | 81.91 (estimated) | -5.6% |
| India | 13.6 | 6.8% |
| Japan | 6.8 | -6.6% |
| U.S. | 6.6 | 1.2% |
| Russia | 6 | -0.6% |
| South Korea | 5.2 | -8.8% |
| Turkey | 3.2 | -1.4% |
| Germany | 2.8 (estimated) | -8.8% |
| Brazil | 2.6 (estimated) | -4.5% |
| Iran | 2.2 | -24.1% |
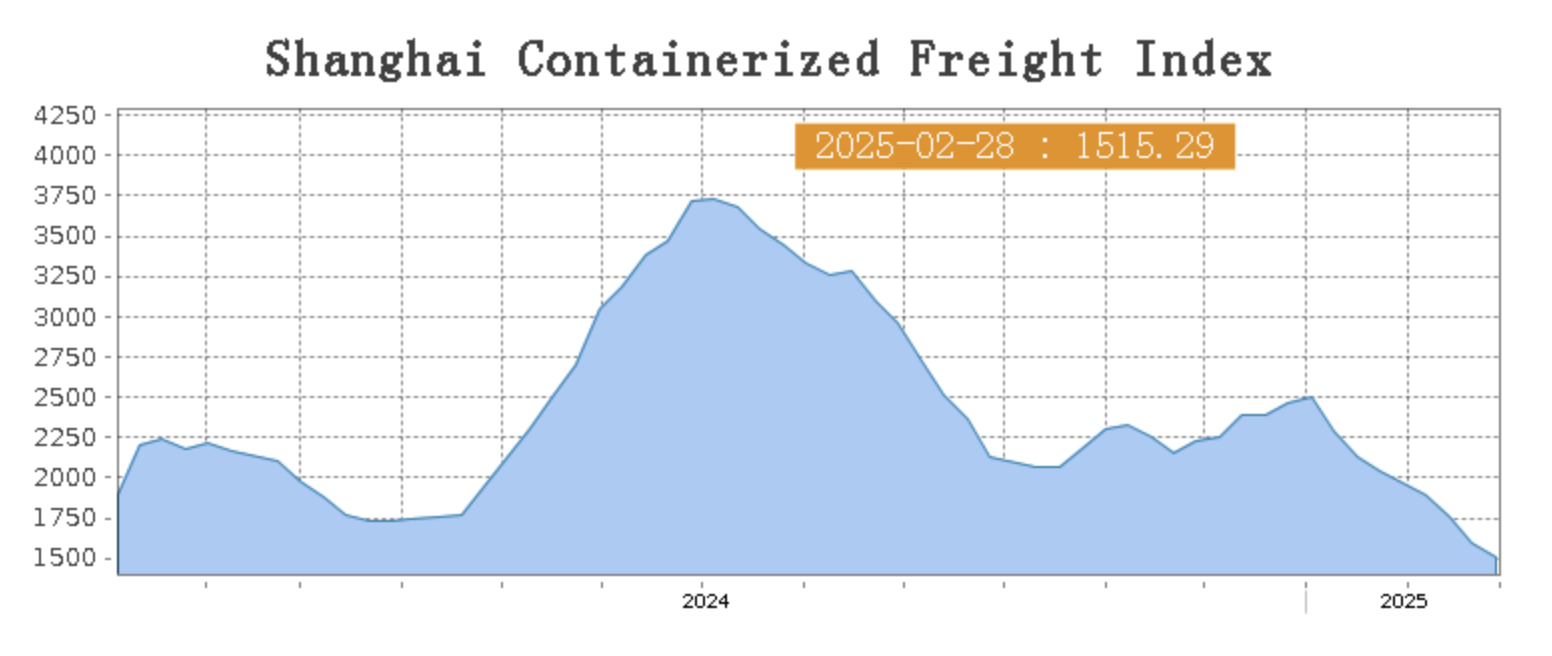
SEA FREIGHT || Weak Growth in Transport Demand, Falling Rates on Most Routes.
Last week, China's export container shipping market continues to experience a slow recovery. Transport demand remains weak, and the overall supply-demand fundamentals are relatively fragile. As a result, freight rates on most routes have continued to decline, dragging down the composite index.
On February 28th, the Shanghai Containerized Freight Index (SCFI) fell 5% to 1515.29 points.
Europe/ Mediterranean:
Germany’s election results last week aligned with market expectations, raising hopes for continued economic recovery in Germany, which could, in turn, stabilize and improve the European economy. Following consecutive rate adjustments, market freight rates saw a rebound last week.
On February 28th, the freight rate (maritime and marine surcharge) exported from Shanghai Port to the European major ports was US$1693/TEU, which rose by 7.3%. The freight rate (shipping and shipping surcharges) for exports from Shanghai Port to the Mediterranean major ports market was US$2594/TEU, which dropped by 1.1%.
North America:
The U.S. tariff hikes have further escalated trade tensions, which may negatively impact the North American shipping market in the future.
On February 28th, the freight rates (shipping and shipping surcharges) for exports from Shanghai Port to the US West and US East major ports were US$2482/FEU and US$3508/FEU, reporting 14.6% and 11.3% down accordingly.
The Persian Gulf and the Red Sea:
On February 28th, the freight rate (maritime and marine surcharges) exported from Shanghai Port to the major ports of the Persian Gulf dipped 7.9% to $1015/TEU.
Australia/ New Zealand:
On February 28th, the freight rate (shipping and shipping surcharges) for exports from Shanghai Port to the major ports of Australia and New plunged 9.6% to $745/TEU.
South America:
On February 28th, the freight rate (shipping and shipping surcharges) for exports from Shanghai Port to South American major ports dropped 6.0% to $2770/TEU.
Worsening Congestion at Vancouver Port.
Congestion at Canada's Port of Vancouver is expected to worsen in the coming weeks due to inland rail network constraints and declining schedule reliability as shipping alliances continue their restructuring from February.
Hapag-Lloyd recently informed customers: “Both CPKC Railway and CN Railway have implemented tiered operational restrictions in response to severe winter weather across Canada.” These measures include shortening train lengths and reducing speeds, leading to minor delays. “These conditions are expected to persist for 10-14 days, resulting in increased import dwell times,” the company added.
The company also reported that utilization at Vancouver's GCT Delta terminal has reached 102%, with vessels experiencing an average berthing delay of nine days. Meanwhile, DP World’s Centerm terminal has an 83% utilization rate, with berthing delays ranging between four and nine days.
Rail restrictions have further prolonged the dwell time for imported containers. Currently, the dwell time at GCT Delta is 4.1 days, while at DP World Centerm, it has extended to 5.9 days.
Temporary Resolution to East Coast Terminal Strike.
On Tuesday, February 25, the International Longshoremen's Association (ILA) voted to approve a new six-year contract. ILA members overwhelmingly ratified the agreement with port employers represented by the United States Maritime Alliance (USMX).
According to an ILA press release, nearly 99% of rank-and-file members voted in favor of the agreement, which covers 24,000 container-handling dockworkers at 14 ports from Boston to Texas. The new contract is retroactive from October 1, 2024, and will remain in effect until September 30, 2030. Under the agreement, wages will cumulatively increase by 62% over the contract period, raising workers' base hourly wages from $39 to $63, making them among the highest-paid blue-collar workers in the U.S.
In addition to wage increases, the new contract improves healthcare and pension benefits while permitting limited automation in container handling, ensuring job security for union workers.
The ILA contract is also expected to set a precedent for future negotiations between the International Longshore and Warehouse Union (ILWU) and the Pacific Maritime Association (PMA), which represent employers on the West Coast.
Currently, the contract for dockworkers at 29 West Coast ports, approved in August 2023, is set to expire on July 1, 2028.










